What is collagen and how does it benefit my health?
Hailed by many as an anti-aging superstar, collagen is taken by lots of people who want younger-looking skin. But what exactly is collagen, how does this protein affect your health and how beneficial are collagen supplements?
What is collagen?
Collagen is the most abundant protein in your body. It forms a scaffold that gives strength and structure to your body. It creates structure within your bones, cartilage, tendons, connective tissue, muscles, and skin. Without collagen, you’ll just be a bunch of cells connected by a few neurons.
Like all proteins, collagen is made up of amino acids. Collagen tends to be high in glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline. Amino acids are shaped like chains and the amino acids in collagen are tightly woven together – like a twisted rope. This strong protein enhances your health in many ways.
Healthy collagen levels contribute to:
- joint health
- protection of the kidneys and other organs
- skin elasticity
- a healthy cardiovascular system
Your body naturally produces collagen but as you get older production drastically decreases and collagen fibres become thinner and weaker. Read on to find out what causes a decline in collagen production.
What causes collagen loss?
The following factors can cause your body to produce less collagen or weaken collagen fibres:
- Hormonal changes due to pregnancy and menopause can cause less collagen to be produced.
- Aging reduces collagen levels. Naturally, your body produces less collagen as you become older.
- Drinking too much alcohol can accelerate aging by reducing collagen production.
- Smoking cigarettes is known to degrade collagen and cause skin aging, wrinkles, and loss of elasticity.
- Ultraviolet rays, from sun exposure, can cause collagen to break down in the skin.
- A diet high in sugar and processed food can also cause lower levels of collagen.
- Vitamin C deficiency. This vitamin is necessary for collagen synthesis, so having low or deficient levels of vitamin C can lead to impaired collagen production.
Taking collagen
Your body makes its own collagen. This is called endogenous collagen.
To boost the amount of collagen in your body, you can eat bone broth, chicken, or egg whites.
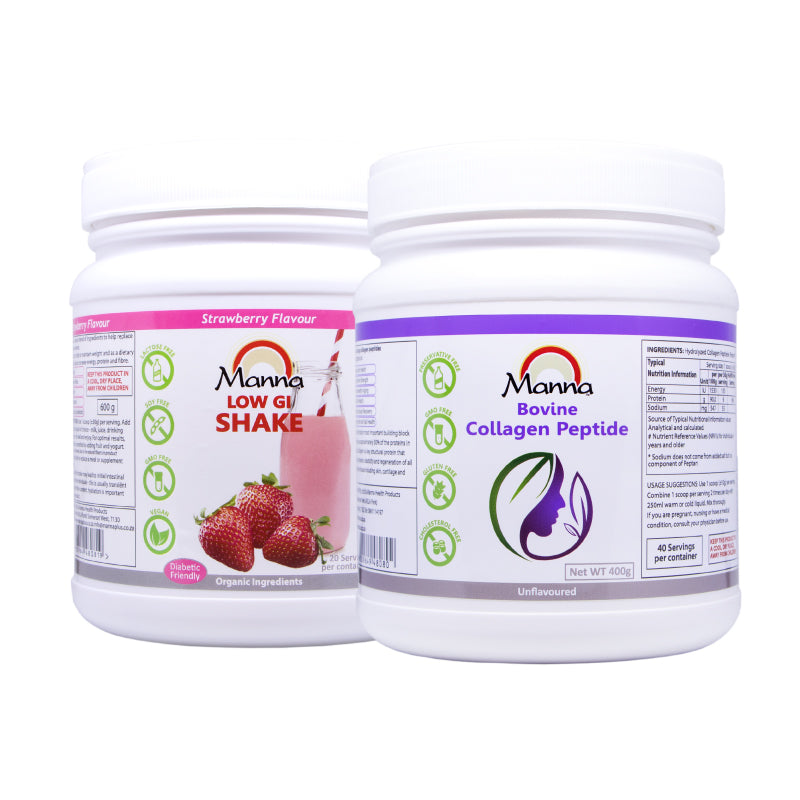
You can also take synthetic collagen. Exogenous collagen comes from an outside source, such as supplements. These supplements are available in many forms like pills, gummies, powders, liquid or in some foods and drinks.
Supplements can help slow down signs of aging such as wrinkles and loss of skin hydration. They can also help with joint pain.
Although lacking in evidence, some people believe that taking collagen supplements can also help with weight loss.
Healthcare professionals also use collagen to help with the treatment of wounds, burns, and diabetic ulcers.
The benefits of collagen supplements
The most common use of collagen supplements is to better skin health. A lot of studies have shown that taking collagen supplements may improve skin hydration and elasticity and reduce the appearance of wrinkles. Most studies suggest taking 2.5–15 grams of collagen per day for 8 weeks or longer.
Collagen supplements may also be especially beneficial to older women with reduced bone mineral density (BMD). Studies suggest that taking collagen supplements long-term may help increase bone mineral density in people in postmenopause, who are at a greater risk of developing osteopenia and osteoporosis. These supplements can also help reduce symptoms of osteoarthritis.
Takeaway
Collagen is a strong protein that functions like scaffolding – giving structure within your bones, cartilage, tendons, connective tissue, muscles, and skin. Collagen keeps your skin and joints elastic. Your body naturally produces collagen but as you get older, you’ll make less of the protein. Taking collagen supplements can help your skin stay elastic and help with joint mobility.