Why Does Low GI Matter for Weight Control?
When your blood sugar spikes, your body releases more insulin—a hormone that tells your cells to store energy, often as fat. The problem? When insulin is working overtime, it’s much harder to burn fat, and you’ll likely feel hungry again sooner. This cycle can create a challenging relationship with food, making it difficult to maintain a healthy weight.
Low-GI foods help by keeping blood sugar levels stable, reducing hunger and curbing cravings. Unlike high-GI foods that cause rapid spikes and crashes, low-GI foods provide a gradual release of energy, which helps keep you feeling satisfied for longer. This means you’re less likely to snack on unhealthy treats or overeat at your next meal. With steady energy, you’ll also feel more motivated to stay active—whether that’s hitting the gym or simply going for a walk after dinner.
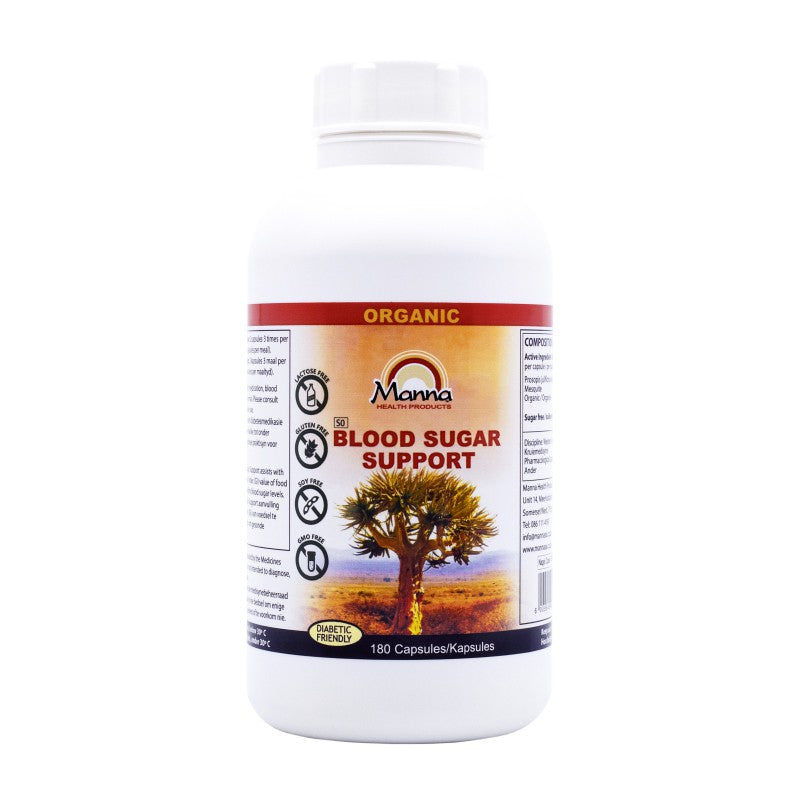
Incorporating low-GI foods into your diet can be a game-changer, particularly when paired with tools like Manna Blood Sugar Support. This supplement can help reduce the glycemic impact of higher-GI foods by promoting better blood sugar regulation, allowing for a more stable release of glucose into the bloodstream and minimising insulin spikes. This combination not only aids in weight control but also enhances overall well-being, making your health journey a lot smoother.
How Low GI Diets and Sugar Spikes Influence the Functioning of Your Body
Low GI Diets:
Following a low GI diet positively influences your body’s functioning in several key ways:
Stable Blood Sugar Levels:
By consuming foods that release glucose slowly, you help maintain balanced blood sugar levels. This stability prevents sudden fluctuations that can lead to energy crashes and irritability.
Reduced Insulin Resistance:
Lower insulin spikes help prevent insulin resistance, a condition where the body becomes less responsive to insulin. Over time, this can reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes and other metabolic disorders.
Improved Satiety:
Low GI foods tend to be more nutrient-dense and high in fiber, promoting a feeling of fullness. This reduces the likelihood of overeating and helps regulate appetite hormones, making it easier to manage weight.
Enhanced Fat Oxidation:
With stable insulin levels, your body can more effectively tap into stored fat for energy, aiding in fat loss and improving overall body composition.
Consistent Energy Levels:
A low GI diet helps maintain steady energy levels throughout the day, which can improve focus, productivity, and overall mood.
Sugar Spikes:
On the other hand, consuming high-GI foods that cause sugar spikes can negatively impact your body’s functioning:
Rapid Blood Sugar Fluctuations:
High-GI foods cause a quick rise in blood sugar, followed by a sharp drop. This rollercoaster effect can lead to fatigue, irritability, and difficulty concentrating.
Increased Insulin Production:
The body releases a significant amount of insulin to manage the sugar spike. Over time, frequent spikes can lead to the overproduction of insulin, increasing the risk of insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome.
Hunger and Cravings: The rapid drop in blood sugar after consuming high-GI foods can trigger intense hunger pangs and cravings for more sugar or carbs, leading to a cycle of overeating and poor food choices.
Fat Storage: Consistently high insulin levels encourage the body to store excess glucose as fat, making it challenging to lose weight and potentially leading to weight gain over time.
Increased Risk of Chronic Diseases: Frequent sugar spikes and subsequent metabolic stress can contribute to a higher risk of chronic diseases, including heart disease, diabetes, and obesity.