How to avoid getting one of the most serious complications of diabetes
Diabetes causes many problems like heart and blood vessel disease, amputation, blindness and diabetic kidney disease (diabetic neuropathy). DKD is a common health complication among people with diabetes as about 30 to 40 percent of diabetes sufferers develop the disease.
DKD is also one of the most serious diabetes complications as it can cause end-stage kidney disease (ESRD), which happens when your kidneys can not function well enough for day-to-day life. People with ESRD have to get dialysis or a kidney transplant.
Luckily not all cases of kidney disease end up with ESRD. Early treatment can be very effective and there are many lifestyle changes you can make to prevent the onset of this disease.
How your kidneys work
Your kidneys’ main job is to remove toxins from your blood and then transform this waste into urine. Your kidneys have millions of tiny, very specialized, blood vessels that filter about 200 litres of fluid every 24 hours. The waste, in the form of urine, is sent to the bladder and vitamins, amino acids, glucose, hormones and other useful substances are returned to the bloodstream. This process is vital to make the body function efficiently.
Other important responsibilities of your kidneys include:
- Keeping the electrolytes (sodium and potassium being the most important) and water content of the body constant
- Helping blood pressure stay under control
- Keeping bones healthy
- Helping make red blood cells
If your kidneys are damaged, they will struggle to perform these tasks. This damage can occur because of high blood sugar levels. High blood sugar levels cause diabetes.
How diabetes damages your kidneys
Over time, especially if you have type 2 diabetes, your kidneys can become overworked because they’re constantly removing excess glucose from your blood. The tiny, specialized blood vessels can get damaged. When this happens, your kidneys will struggle to filter the blood passing through. Later, blood vessels can become leaky and protein that was supposed to be reabsorbed into your bloodstream gets excreted through your urine. The most common protein found in urine is called albumin.
The symptoms of DKD
Diabetic kidney disease is difficult to detect as there are usually no onset symptoms. If you want to know if your kidneys are damaged, your doctor can do a urine test to see if there is any protein in your urine that leaked from the tiny blood vessels in your kidneys.
Having a small amount of albumin in your urine is referred to as microalbuminuria. When larger amounts of albumin are found in your urine, the condition is called albuminuria (macroalbuminuria) or proteinuria.
Because DKD does not have any onset symptoms you need to get tested frequently if you have diabetes. If you’re living with type 1 diabetes, screening for diabetic nephropathy is recommended beginning five years after your diagnosis. If you are diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, screening will begin at the time of diagnosis.
Later stages of DKD are associated with the following symptoms:
- Worsening blood pressure control
- Swelling of feet, ankles, hands or eyes
- Increased need to urinate
- Reduced need for insulin or diabetes medicine
- Confusion or difficulty concentrating
- Shortness of breath
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea and vomiting
- Persistent itching
- Fatigue
How to prevent DKD
DKD is a serious health complication of diabetes but fortunately, there are many changes you can make to prevent the onset of this disease.
1. Treat your diabetes
Talk to your doctor about whether you should take diabetes medication or insulin.
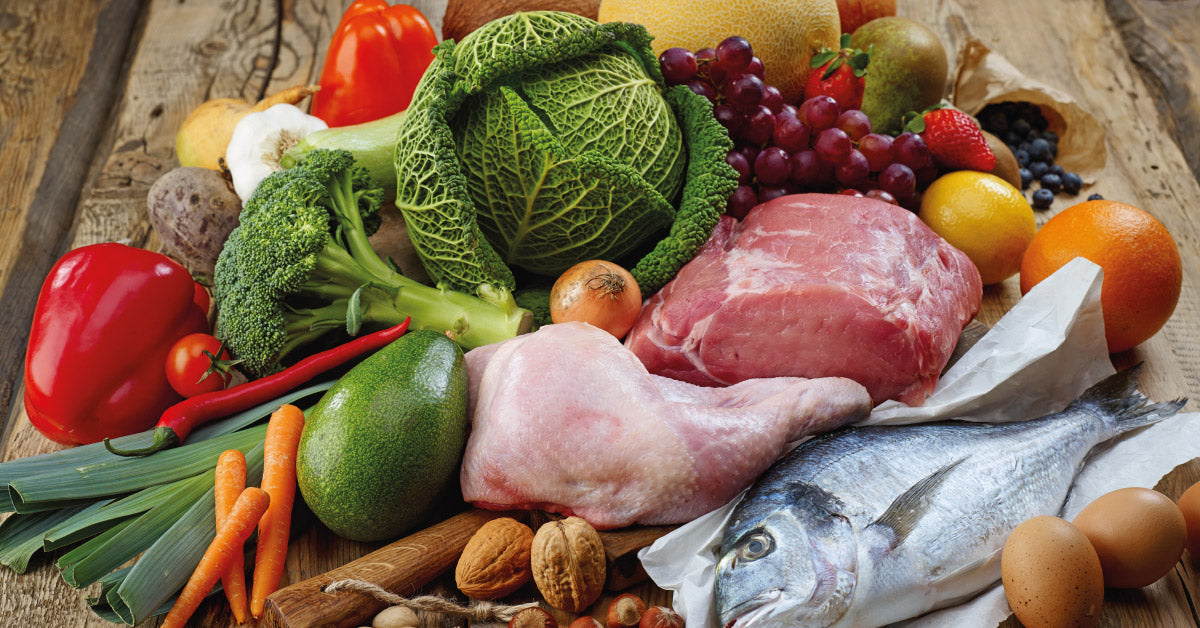
You can also dramatically improve your condition by making lifestyle changes like:
- Eating low GI foods like green vegetables, most fruits, raw carrots, kidney beans, chickpeas, and lentils
- Exercising every day for about 30 minutes
- Lose weight
- Manage your stress levels
- Keep tabs on your blood sugar levels
2. Control your blood pressure
High blood pressure can constrict and narrow the blood vessels in your kidneys. Lifestyle changes like weight loss, exercise, and stress management help. Reducing salt intake is also important. Medication may be needed to control blood pressure.
3. Eat less protein
Eating too much protein can make your kidneys work harder. About 10 to 20 percent of your calories should come from protein.
4. Quit smoking
Smoking is a risk factor for diabetic neuropathy. Talk to your doctor about strategies for quitting.
5. Treat urinary tract infections right away
If you experience frequent urination, pain when urinating, or cloudy or blood-spotted urine, you might have an infection. Treat infections promptly to avoid kidney damage.
Takeaway
DKD is one of the most serious diabetes health complications. Fortunately, there’s a lot you can do to prevent or slow its progress. Taking care of your blood sugar levels and making healthy lifestyle changes are key.